
Buying a new laptop isn’t just about design, display, or brand anymore. The real performance of a laptop comes from what’s inside — the processor.
And that’s where most people get confused.
Intel and AMD?
At first, it sounds like a small technical choice. In reality, the processor directly affects:
- How fast your laptop feels
- How smoothly it handles multitasking
- Battery life
- Heat and fan noise
- Long-term reliability
Choose the right processor, and even a mid-range laptop feels quick for years.
Choose poorly, and even an expensive machine can feel slow over time.
So instead of complicated benchmarks and technical jargon, let’s look at this practically — how Intel and AMD compare in everyday use, and which one makes sense for different types of users.
Why the Processor Matters So Much
You can think of the processor as the brain of your laptop.
Every task depends on it:
- Opening apps
- Running Chrome tabs
- Online meetings
- Editing photos or videos
- Gaming
- Working with Excel or coding
Many buyers focus only on RAM or storage, but the truth is simple:
A weak processor cannot be fixed by adding more RAM. That’s why two laptops with similar prices and specs can feel completely different in speed. Understanding the CPU first helps you make a smarter purchase.
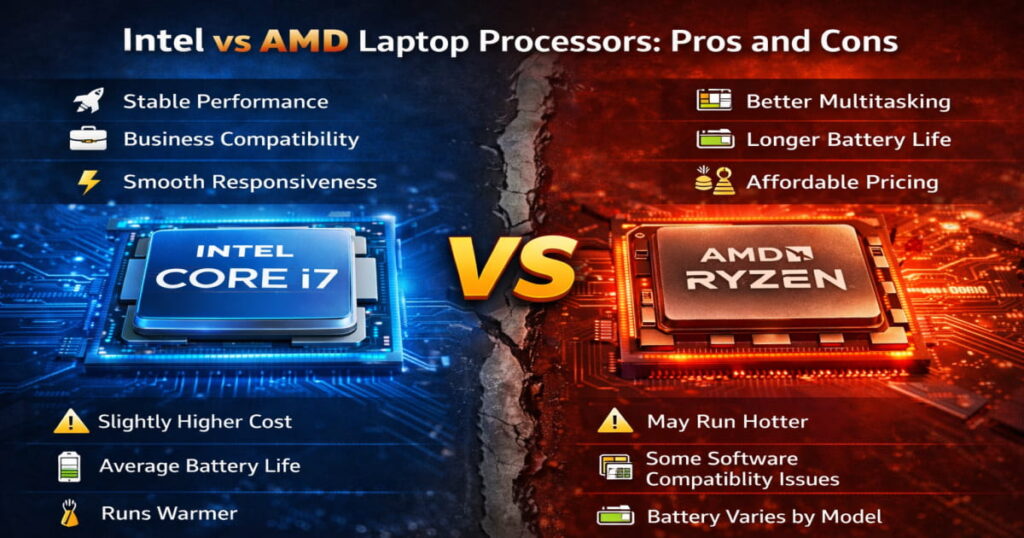
Intel Processors: Stable and Consistent
Intel has been the default choice in laptops for many years. Because of that long history, it’s often seen as a safe and reliable option.
For tasks like:
- Office work
- Web browsing
- Online classes or meetings
- Light coding
- General productivity
An Intel Core i5 or i7 is more than enough and usually feels very smooth.
For tasks like:
- Office work
- Web browsing
- Online classes or meetings
- Light coding
- General productivity
An Intel Core i5 or i7 is more than enough and usually feels very smooth.
Things to keep in mind
Compared to similar AMD options, Intel laptops can sometimes:
- Cost slightly more
- Consume more power under heavy load
- Run warmer
- Offer average battery life in mid-range models
This doesn’t make Intel worse — it just means you may pay a bit extra for similar performance.
AMD Processors: Performance and Efficiency Focused
AMD’s position in laptops has improved significantly in recent years, especially with the Ryzen series.
Modern Ryzen processors focus on:
- More cores and threads
- Better power efficiency
- Competitive pricing
In real-world usage, this often translates into smoother multitasking and better battery life.
AMD processors are particularly strong for:
- Heavy multitasking
- Many browser tabs
- Video editing or designing
- Gaming
Students and budget buyers
Because of the extra cores, Ryzen systems tend to handle multiple tasks more comfortably without slowing down. They also generally run cooler and last longer on battery.
For many users, this balance of performance and price makes AMD very attractive
Understanding Processor Series
A common mistake is focusing only on Intel and AMD while ignoring the processor series. The series often matters more than the brand.
Intel
- U series → battery efficient, everyday use
- P series → balanced performance
- H/HX series → high performance (gaming, editing, heavy tasks)
AMD
- U series → efficient and longer battery
- HS/H series → performance focused
- HX series → maximum performance
Simple guideline
- Long battery life → U series
- Balanced daily use → P/HS
- Heavy workloads → H/HX
Choosing the wrong series (for example, buying an H-series for basic browsing) can reduce battery life unnecessarily.
Real-World Difference in Daily Use
Here’s something many buyers don’t realize:
For basic tasks, both Intel and AMD feel almost identical. If your work includes browsing, watching videos, and using Office apps, you likely won’t notice any difference between an Intel i5 and a Ryzen 5.
The difference becomes noticeable during heavier workloads:
- multitasking with many apps
- editing photos or videos
- long working sessions
- gaming
In these cases, AMD’s extra cores and efficiency often provide slightly smoother performance and better battery backup. Intel still performs well, but AMD frequently offers similar or better performance at a lower price.
Intel and AMD Laptop Processors: Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Intel | AMD |
|---|---|---|
| Everyday Performance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Multitasking | Good | Slightly Better |
| Gaming Value | Good | Better for Price |
| Battery Life | Average | Longer |
| Heat Management | Moderate | Cooler |
| Price | Slightly Higher | More Affordable |
Both are strong options — each just has different advantages.
Which Processor Suits Different Users?
| User Type / Usage | Recommended Processor |
|---|---|
| Students & Casual Users | Ryzen 5 or Intel Core i5 (U series) |
| Office & Business Work | Intel Core i5/i7 or Ryzen 5/7 |
| Multitasking & Content Creation | Ryzen 7/9 or Intel Core i7 H-series |
| Gaming | Performance series (H/HX) with dedicated GPU |
| Long Battery Life Priority | Ryzen U-series laptops |
In most cases, selecting the right configuration matters more than the processor brand.
Things Worth Checking Before Choosing a Laptop
A processor alone doesn’t guarantee good performance.
Make sure the overall setup is balanced:
- At least 16GB RAM (8GB minimum today)
- SSD storage
- Proper cooling
- Latest processor generation
- Suitable series (U/H/P)
- Decent battery capacity
Even the best CPU can feel slow in a poorly configured laptop.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Buying older generation processors
- Choosing high-performance chips without needing them
- Ignoring RAM or SSD
- Paying extra only for brand name
- Getting non-upgradable 8GB laptops
Avoiding these small mistakes can significantly improve long-term performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better overall, Intel or AMD?
- Both are reliable. AMD often offers better value and battery life, while Intel is known for consistent stability.
Is AMD faster than Intel?
- For multitasking and heavy workloads, AMD may perform better. For daily use, both feel similar.
Which processor is good for students?
- Ryzen 5 or Intel i5 U-series processors are ideal.
Is processor more important than RAM?
- Both matter. A balanced combination gives the best experience.
Final Thoughts
Today, both Intel and AMD make capable and dependable processors. There is no clear “wrong” choice anymore.
For most users, AMD currently offers slightly better value and efficiency.
Intel remains a dependable and widely trusted option.
Instead of focusing only on the brand, focus on:
- the right processor tier
- latest generation
- sufficient RAM
- SSD storage
- overall laptop quality
Choose based on your needs, and either platform can serve you well for years.





Pingback: Best Laptop Processors for Students in 2026